How does Controlling play a Significant Role in Companies' Business Administration Success or Failure…?
Controlling in business management is a very important process in a company’s Business Administration! It definitely plays a role in every step a company takes towards achieving its goals successfully.
Controlling is essential in every process for it always reduces the risks of errors that might occur, however, in business administration, controlling has the major role of redressing the faults and defects and redirecting the work towards the right track.
Here is a review of “controlling” as a concept, and the concepts that follow:

Generally, managing the important activities and functions in a company is entrusted to people who are most aware of the company’s objectives, strategies, and projects. One of these functions and the most influential in business administration is controlling; which holds the actual responsibility of leading the actions properly to achieve the company’s goals professionally and successfully.
What is Controlling in business managment ?
Pioneers in the field of administration like; “Tareq Taha, Suad Naef Al-Barnoti, Ismail Hamid and others…” have set many definitions for the function of controlling! As a result, we can define
Controlling is an organized group of actions that concentrates on making efforts to keep the pace of operations' progress in the company, making sure that the operations are carried out accordingly to the requirements, and predefined standards and criteria which are mainly related to the cost, quality and time. And at a certain point in time, performance is subject to be measured and compared to the company's plan in order to detect deviations and find out their underlying causes, then use the perfect options from the available solutions to fix the problems. In addition to predicting possible future problems and finding out vital solutions before they might even happen. All these procedures will first and foremost achieve the goals of the company successfully.
Thus, Controlling, as a business function, basically depends on information comes from data resulting from regular measuring and comparing between the projects’ actual performance and the required one, to bring to light the weaknesses and strengths and deduce the misapply and errors, in order to reach the stage of taking the right decision and implement it as soon as possible.
So, controlling has to keep an eye on plans, programs and activities to guarantee they are compatible with the company’s overall environment, taking into consideration the company’s objectives including (cost, quality and time), and the company’s resources (material, financial and human).
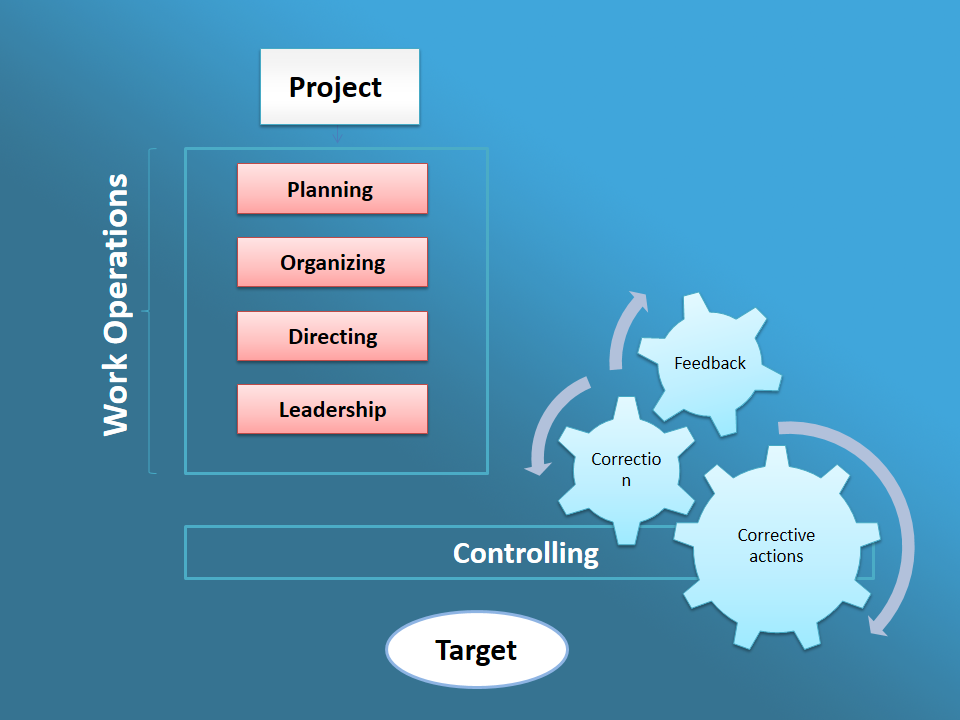
Controlling depends on the feedback received from the circumstances and reasons that hinder goals’ achievement process, then tries to solve problems, reconsider the methods, or even create better and more appropriate techniques.
Stages of Controlling:
- Set standards: The first step is to set the main plan, manage costs and timing, then allocate tasks and responsibilities to personnel and workers.
- Measure performance is the next step in controlling, in which the performance progress is measured in terms of quantity and quality by an Integrated Performance Measurement Systems, with reference to that the “Earned Value Management – EVM” is the best appliance for controlling the works’ progress.
- Compare performance with standards and identify deviation: The third step is a delicate phase and requires accuracy, prediction, and correct measurements of quality and quantity. Controlling here is checking current performance against the pre-determined standards contained in the plan to figure out the deviations and judge whether they are good or bad, allowed or rejected, to ensure adequate progress and satisfactory performance.
- Correct deviations: The last step is to correct the faults and deviations, and adjust the plan if needed. Doing so goes through one of these ways:
- Keep the current situation
- Make corrective adjustments to the main criteria
- Radically change the standards and criteria
It is worth mentioning that figuring out errors and deviations remains ineffective unless followed by corrective processes to get the works back on the right track again.
Types of Controlling
The most common logical way to classify controlling types is classifying according to time… with such classification we can mention 3 types:
- Preventive or Pre-emptive control : This type of control is the best; for it attempts to predict deviations and faults before they occur, depending on accurate and valid data and information received from the system of controlling.
- Progress or Corrective Control is also a preferable type of control. It follows up the track of operations’ progress thoroughly to detect and correct the faults and deviations immediately. So, it doesn’t use prediction which considered a precise and difficult task. Information in this type is collected from plans, schemes, proposals and schedules.
- Detective or Output Control: This type is the least preferable, yet it is considered useful for future improvements and opportunities. It won’t change acts have taken a place, but can avoid same deviations reoccurring. Objectives, recommendations and final reports are the tools this type of controlling relies on.
Controlling Methods and Techniques
Controlling system works through a variety of methods and techniques that differ according to the company, controller in charge, and accuracy of the controlling system, So that; controlling can be:
- Descriptive: It depends on using graphs and charts to illustrate its stages and results. This technique is suitable for corporations and mega projects.
- Field (On-Site): It depends on the reports presented by controllers in charge who conduct inspection rounds to look over the actual situation. This controlling method can be used in companies that adopt small projects.
- Quantitative: It is to monitor the estimated budgets submitted by the responsible sections step by step during the business progresses.
- Networked: It is about drawing networks in certain styles in order to study the cost and time of the company’s various activities, and come up with a result that is very compatible to the controlling system. Such as Pert chart and Critical Path Method (CPM).
As in every administrative system, the system of controlling may succeed or fail due to various factors, and that’s what we will discuss in a future article.
Finally, it should be noted that controlling in business management is concerned with every detail that may affect directly or indirectly the performance of the company, whether it is related to material or human resources, suppliers and customers, marketing and promotion, or any other ongoing process in the company.









